fConsider a course with 40 students....
Consider a course with 40 students, some of whom are confused after the professor explains a concept. The professor doesn't know whether students are confused, but will clarify the concept if one student asks a question. A student who asks a
questionlong dash—and
reveals his or her
confusionlong dash—loses
88
utils. When the professor clarifies the concept in response to a question, each confused student gets a benefit of
22
utilsutils.
a. A question from a confused student will be socially efficient if 5 students in the classroom are confused. (Enter your response as an integer.)
b. In the absence of participation incentives, will a confused student ask a question when it would be socially efficient to do so?
No
c. Which of the following incentive systems would be most likely to generate efficient questioning?
A.
Confused students who do not ask the question must compensate the confused student who does ask the question.
B.
Confused students appeal to each other's sense of civic or moral responsibility.
C.
Confused students agree to take turns asking questions.
D.
All of the above.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is true about unemployment?
a. the benchmark high-employment level is most likely between 3 and 4 percent b. In recent years, the appropriate benchmark high-employment level has risen. c. Based on the experience of the 1960s, a 7 percent unemployment rate was too low to be sustained without a buildup of inflationary pressure d. During the 1970s, the benchmark high-employment level rose but this was not observed by economists at the time.
If we were on curve J, the lowest three quintiles received about _____% of income.
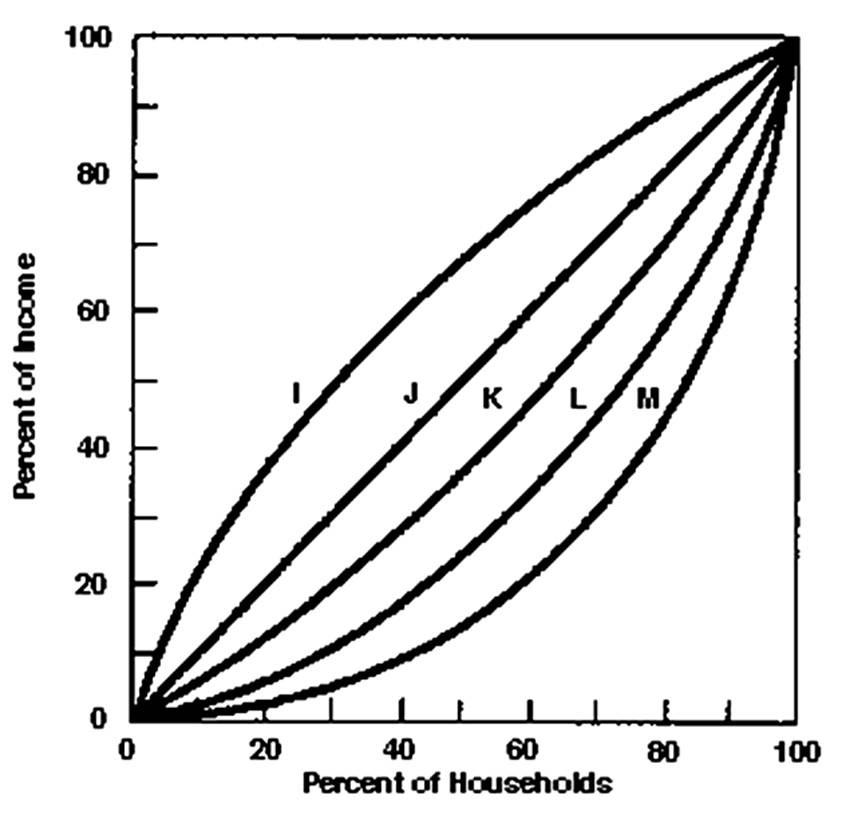
A. 20
B. 40
C. 50
D. 60
You are the CEO of a U.S. firm considering building a factory in Chile. If the dollar appreciates relative to the Chilean peso, then other things the same
a. it takes fewer dollars to build the factory. By itself building the factory increases U.S. net capital outflow. b. it takes fewer dollars to build the factory. By itself building the factory decreases U.S. net capital outflow. c. it takes more dollars to build the factory. By itself building the factory increases U.S. net capital outflow. d. it takes more dollars to build the factory. By itself building the factory decreases U.S. net capital outflow.
Which of the following supply shocks would shift the aggregate supply curve inward?
What will be an ideal response?