Refer to the information provided in Figure 9.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 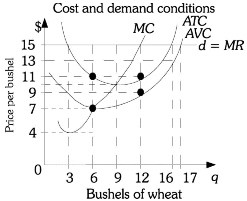 Figure 9.1Refer to Figure 9.1. If this farmer maximizes profits, his per-bushel profit will be
Figure 9.1Refer to Figure 9.1. If this farmer maximizes profits, his per-bushel profit will be
A. $2.
B. $4.
C. $9.
D. $15.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suzi is a British citizen who works for Yankee Candles in Massachusetts. Suzi's work will be included in:
A. U.S. GDP since she's working for a U.S. firm. B. U.S. GDP since she's working for a firm located in the U.S. C. England's GDP since she's a British citizen. D. both the U.S. and England's GDP.
The height of the supply curve at a quantity of 100 represents the
a. total value of all 100 units to consumers. b. minimum price required to induce a producer to supply the hundredth unit. c. equilibrium price of the good regardless of the position of the demand curve. d. profit derived by producers from the sale of the hundredth unit.
Suppose a 50-seat bus is about to depart from Boston to New York with five empty seats. The total cost to the bus company of the trip is $1,000 regardless of how many people are on the bus and no services, food, or beverages are provided to passengers. Use marginal analysis to develop conditions under which the bus company would be willing to sell tickets for the five remaining seats.
A. The bus company would be willing to sell the five remaining tickets at a price of at least $20 each to cover the cost per seat of those passengers. B. The bus company would be willing to sell the five remaining tickets at any price over $0 because there is no additional cost of five more passengers. C. The bus company would not be willing to sell the five remaining tickets because it already covered the cost of the trip with the revenue from the 45 passengers on board. D. The bus company would be willing to sell the five remaining tickets at a price of at least $25 each because they need to make a profit on each passenger.
The Phillips curve trade-off relationship implies that
A. the government can fine-tune the economy and pick the most preferred combination of unemployment and inflation. B. there is no relationship between inflation and unemployment, at least in the long run. C. low unemployment can be obtained only by generating rapidly increasing inflation. D. the government can fine-tune the economy and generate both the natural rate of unemployment and zero inflation.