The concept of diminishing marginal benefits means that? __________.
A. the more of a good that you? consume, the lower is your overall benefit from that good.
B. each additional unit consumed is worth less to you than the previous one.
C. each additional unit consumed is worth more to you than the previous? one, but the additional benefit grows at a diminishing rate.
D. as you consume more of a? good, your willingness to pay for that good increases faster than the benefit you receive.
B. each additional unit consumed is worth less to you than the previous one.
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the next question. 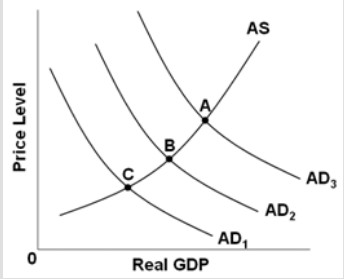 The economy is at equilibrium at point B. What would expansionary fiscal policy do?
The economy is at equilibrium at point B. What would expansionary fiscal policy do?
A. Move the economy from point B towards point C. B. Move the economy from point B towards point A. C. Move the economy from point B downward along AD2. D. Move the economy from point B upward along AD2.
If oil refiners expect the government to tax away any profits created by international supply disruptions, refiners will choose to
A) carry smaller inventories of crude petroleum. B) leave the oil refining business. C) prevent the price of crude petroleum from rising. D) raise their prices to cover their added risks. E) take a higher percentage of their profits as windfalls.
Topic Market failure, Difficulty M, Type RE, Answer c Which of the following is not an example of market failure?
a. Lack of competition. b. Externalities. c. Equilibrium. d. Extreme income inequality.
If the shifts in AD that will result from policy changes are fully and accurately anticipated, an increase in government purchases or a decrease in taxes would result in which of the following in the short run?
a. a higher level of real output and a higher price level b. a higher level of real output but no change in the price level c. a higher price level and a reduced level of real output d. a higher price level but no change in real output