At the beginning of year one, there is no government debt outstanding. The government runs a $100 billion deficit in year one. Interest at a nominal rate of 10% must be paid starting in year two. Assume nominal GDP in year one is $2000 billion and the nominal growth rate of GDP is 4%. Assume the government balances its primary budget in the future and the interest rate and growth rate do not change.(a)What will be the government deficit in years two, three, four, and five?(b)What will be the value of government bonds outstanding at the end of the fifth year?(c)What will be the debt-GDP ratio at the end of year five?
What will be an ideal response?
| (a) | $10, $11, $12.1, $13.31 (all in billions) |
| (b) | $146.41 billion |
| (c) | 0.0626 |
You might also like to view...
________ theory relates the quantity of money and monetary policy to changes in aggregate economic activity and inflation
A) Monetary B) Fiscal C) Financial D) Systemic
For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, a price decrease:
A. increases the profit-maximizing quantity. B. lowers the profit-maximizing quantity. C. is unrelated to the profit-maximizing quantity. D. signifies the firm should leave the market.
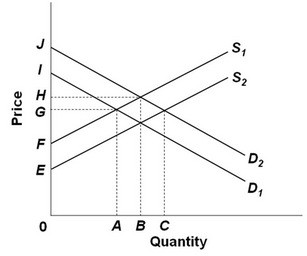 Refer to the above supply and demand graph. Point A represents the current equilibrium level of output of this product and point B represents the optimal level of output from society's perspective. The amount of the subsidy to be given to producers to correct this externality problem would be:
Refer to the above supply and demand graph. Point A represents the current equilibrium level of output of this product and point B represents the optimal level of output from society's perspective. The amount of the subsidy to be given to producers to correct this externality problem would be:
A. EF. B. AB. C. IJ. D. GH.
For an addictive drug such as heroin, if the price of heroin increases, then
A. the quantity demanded never changes. B. the quantity demanded will decrease by a relatively small amount. C. the quantity demanded will actually increase. D. the quantity demanded will decrease by a relatively large amount.