The aggregate demand curve tends to be
a. vertical.
b. horizontal.
c. upward sloping.
d. downward sloping.
d. downward sloping.
You might also like to view...
Willingness to pay:
A) is the lowest price that a buyer is willing and able to pay for a unit of good. B) is the highest price that a buyer is willing and able to pay for a unit of good. C) is equal to the price of the lowest-priced goods in a consumption bundle. D) is equal to the price of the highest-priced goods in a consumption bundle.
Consumer surplus is the:
A) difference between the buyer's reservation value and the price he actually pays. B) product of a buyer's reservation value and the price he actually pays. C) sum of a buyer's reservation value and the price he actually pays. D) ratio of a buyer's reservation value to the price he actually pays.
Using Figure 1 below, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be:
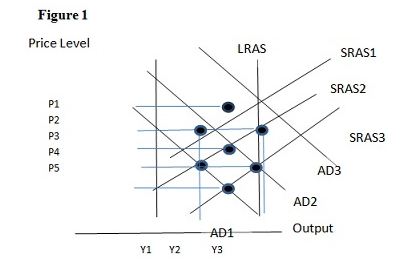
A. P1 and Y2.
B. P3 and Y1.
C. P2 and Y3.
D. P2 and Y2.
The normal life cycle pattern of income
a. contributes to more inequality in the distribution of annual income and to more inequality in living standards. b. contributes to more inequality in the distribution of annual income, but it does not necessarily contribute to more inequality in living standards. c. contributes to less inequality in the distribution of annual income and to less inequality in living standards. d. has no effect on either the distribution of annual income or on living standards.