As air rises, it cools and clouds can form. The rate of cooling determines the elevation of cloud formation and cloud thickness. From first to last, the rates of cooling are
A) dry adiabatic lapse rate—cloud base; moist adiabatic lapse rate—cloud thickness; environmental lapse rate—upper limit of cloud.
B) moist adiabatic lapse rate—cloud base; dry adiabatic lapse rate—cloud thickness; environmental lapse rate—upper limit of cloud.
C) environmental lapse rate—cloud base; moist adiabatic lapse rate—cloud thickness; dry adiabatic lapse rate—upper limit of cloud.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
At extremely high densities and temperatures, electrons can be forced to fuse with protons. This reaction produces
a. hydrogen. b. helium and energy. c. degenerate electrons. d. neutrons and neutrinos. e. large amounts of radio radiation.
Which of the following stars will live longest?
A) 1 solar-mass star B) 2 solar-mass star C) 3 solar-mass star D) 4 solar-mass star
If ? = 40°, ? = 60°, and M = 4.0 kg, determine the tension in string 1.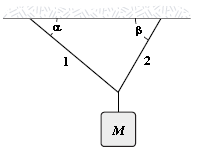
A. 15 N B. 22 N C. 17 N D. 20 N E. 36 N
The radioactivity due to carbon-14 measured in a piece of a wooden casket from an ancient burial site was found to produce 20 counts per minute from a given sample, whereas the same amount of carbon from a piece of living wood produced 160
counts per minute. The half-life of carbon-14, a beta emitter, is 5730 years. Thus we would estimate the age of the artifact to be about A) 5,700 years. B) 11,500 years. C) 14,800 years. D) 17,200 years. E) 23,000 years.