A 2.0-kg block slides on a rough horizontal surface. A force (magnitude P = 4.0 N) acting parallel to the surface is applied to the block. The magnitude of the block's acceleration is 1.2 m/s2 . If P is increased to 5.0 N, determine the magnitude of the block's acceleration
a. 2.1 m/s2
b. 2.3 m/s2
c. 1.9 m/s2
d. 1.7 m/s2
e. 3.2 m/s2
d
You might also like to view...
Exhibit 11-1
Two birds of prey hurtling after the same mouse collide in mid-air and grab each other with their talons. Each 250-g bird is flying at 30 m/s at a 60° angle to the ground.
?
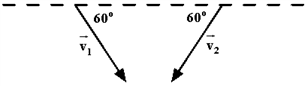
A. 0 B. 6.5 C. 7.5 D. 13 E. 15
A 5-gallon container of water (approximately 20 kg) having a temperature of 212°F is added to a 50-gallon tub (approximately 200 kg) of water having a temperature of 50°F. What is the final equilibrium temperature (in °C) of the mixture?
a. 54 b. 36 c. 18 d. 66 e. 14
Star A is identical to Star B, except that Star A is twice as far from us as Star B. Therefore,
A) both stars have the same luminosity, but the apparent brightness of Star B is twice that of Star A. B) both stars have the same apparent brightness, but the luminosity of Star B is four times that of Star A. C) both stars have the same luminosity, but the apparent brightness of Star A is four times that of Star B. D) both stars have the same luminosity, but the apparent brightness of Star B is four times that of Star A.
A car accelerates from 10.0 m/s to 30.0 m/s at a rate of 3.00 m/s2. How far does the car travel while accelerating?
A) 80.0 m B) 133 m C) 226 m D) 399 m