Some economists believe that the good times of the early 2000s were not sustainable because they were creating a dangerous financial bubble and trade deficit.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
This view has lead some economists to require policy makers to deal with structural changes in the economy in order to get the economy back to the proper level of potential output.
You might also like to view...
All else equal, relative to a person who earns minimum wage, a person who earns $30 per hour has:
A. a lower opportunity cost of driving farther to work. B. a higher opportunity cost of taking the day off work. C. the same opportunity cost of spending time on leisure activities. D. a higher opportunity cost of working an additional hour.
Sam quits his job as an airline pilot and opens his own pilot training school. He was earning $40,000 as a pilot. He withdraws $10,000 from his savings where he was earning 6 percent interest and uses the money in his new business. He uses a building he owns as a hangar that he could have rented out for $5,000 per year. He rents a computer for $1,200, buys office supplies for $500, rents an
airplane for $6,000 . pays $1,300 for fuel and maintenance, and hires one worker for $30,000 . Sam's total revenue from pilot training classes equaled $90,400 . Sam's implicit costs for this year are equal to a. $84,400 b. $39,000 c. $55,000 d. $45,600 e. $40,000
If tax revenues equal 20 percent of total output and government expenditures equal 25 percent of total output, then there is a:
A. trade surplus. B. trade deficit. C. government budget deficit. D. government budget surplus.
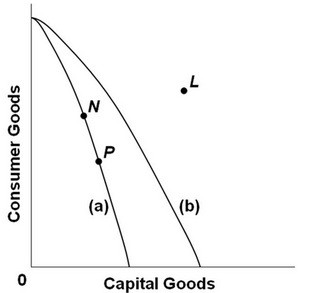 Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. The movement from curve (a) to curve (b) suggests:
Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. The movement from curve (a) to curve (b) suggests:
A. a movement from unemployment to full employment. B. a decline in the total output of this society. C. an improvement in consumer goods technology but not in capital goods technology. D. an improvement in capital goods technology but not in consumer goods technology.