An ice cube in a glass of water is pushed to the bottom of the glass and held there with a straw. Consequently, the buoyant force on the ice cube is now
A. the same as when the cube was floating at the top.
B. exactly balanced by the force exerted only by the straw.
C. exactly balanced by the weight of the ice cube.
D. greater than when the cube was floating at the top.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
A uranium nucleus (mass 238 units) at rest decays into a helium nucleus (mass 4.0 units) and a thorium nucleus (mass 234 units). If the speed of the helium nucleus is 1.8 × 10^6 m/s, what is the speed of the thorium nucleus?
a. 1.0 × 10^4 m/s c. 3.6 × 10^4 m/s b. 3.1 × 10^4 m/s d. 4.1 × 10^4 m/s
What is the equivalent resistance between points a and b when R = 13 ??
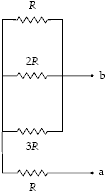
a.
29 ?
b.
23 ?
c.
26 ?
d.
20 ?
e.
4.6 ?
PCM thermal storage systems can be used to store thermal energy from solar energy collectors. The solar collector heats water and the hot water is then passed through the PCM for storage. Then, energy is extracted by passing cold water through the tubes to heat that water. For a system using a PCM having a phase change at 95ºF, with cold water at 65ºF passing through the tubes, and with Bi = 30, NTU = 8, and Fr0 = 0.6, determine the outlet water temperature. Assume tubes have a square arrangement with spacing of 2D.
What will be an ideal response?
Two electric charges each equal to +Q, are separated by a distance d. If you make a graph of the electric potential as a function of the distance along the line connecting the two charges, the point exactly midway between the two charges would
A) be a relative maximum. B) be a relative minimum. C) be neither a relative maximum nor a relative minimum. D) oscillate between being a relative maximum and a relative minimum.