A satellite orbits the earth at a distance of 10,000 miles from the earth's center. At this distance the force of gravity on the satellite is 90 lbs. (a) What would the force on the satellite be if the distance were 5,000 miles instead? (b) At what distance from the earth's center would the force on the same satellite be 10 lbs?
(a) 360 lbs, (b) 30,000 miles
You might also like to view...
Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: An object with a mass of 10 kg is initially at rest at the top of a frictionless inclined plane that rises at 30° above the horizontal. At the top, the object is initially 8.0 m from the bottom of the incline, as shown in the figure. When the object is released from this position, it eventually stops at a distance d from the bottom of the inclined plane along a horizontal surface, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the horizontal surface and the object is 0.20, and air resistance is negligible. Find the distance d.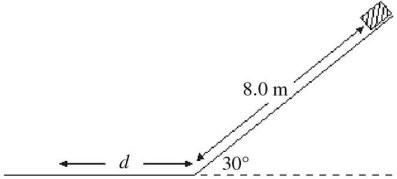
A. 5.0 m B. 10 m C. 15 m D. 20 m E. 25 m
In a contest, two tractors pull two identical blocks of stone the same distance over identical surfaces. However, block A is moving twice as fast as block B when it crosses the finish line. Which statement is correct?
A. Block A has twice as much kinetic energy as block B. B. Block B has lost twice as much kinetic energy to friction as block A. C. Block B has lost twice as much kinetic energy as block A. D. Both blocks have had equal losses of energy to friction. E. No energy is lost to friction because the ground has no displacement.
As water in a confined pipe speeds up, the pressure it exerts against the inner walls of the pipe
A) increases. B) decreases. C) remains constant if flow rate is constant. D) none of the above
Tricia puts 66 g of dry ice (solid CO2) into a 2.0-L container and seals the top. The dry ice turns to gas at room temperature (20°C). Find the pressure increase in the 2.0-L container. (One mole of CO2 has a mass of 44 g and R = 0.0821 L•atm/mol•K. Ignore the initial volume of the dry ice.)
a. 6.0 atm c. 18 atm b. 12 atm d. 2.0 atm