One kg of liquid water at 25°C, for which 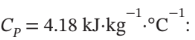
(a) Experiences a temperature increase of 1 K. What is 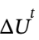 , in kJ?
, in kJ?
(b) Experiences a change in elevation ?z. The change in potential energy 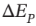 is the same as
is the same as 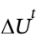 for part (a). What is ?z, in meters?
for part (a). What is ?z, in meters?
(c) Is accelerated from rest to final velocity u. The change in kinetic energy 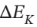 is the same as
is the same as 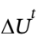 for part (a). What is u, in
for part (a). What is u, in 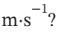
In the previous problems, the heat capacity of water was given as 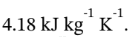 For liquids,
For liquids, 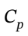 and
and 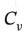 are very
are very
nearly the same, so it doesn’t matter whether this change occurs at constant P or at constant V. The change in internal energy is thus
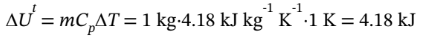
a. The change in gravitational potential energy is
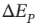 = mg?z
= mg?z
So, to have the same change in potential energy as the change in internal energy in part (a), we need
4180 J = 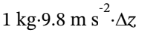
from which ?z = 427 m (or 1400 feet)
b. This time, we need 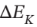
= 1?2mv 2 = 4180 J, from which 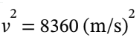 or v = 91.4 m/s (or 205 miles per hour).
or v = 91.4 m/s (or 205 miles per hour).
What have we learned? We have discovered again that what corresponds, in our everyday experience, to a small amount of thermal energy corresponds to a relatively large amount of mechanical energy. The amount of energy required to heat a quart of water (1 kg of water is about 1 liter or 1 quart) from room temperature to its boiling point (increasing the temperature by about 75 K) would be enough to raise the water to a height of about 20 miles (in a frictionless world, or one in which we lifted the object very slowly so that the drag of the air on it was negligible).
You might also like to view...
List six examples of administrative controls.
What will be an ideal response?
Why is there a potential of 24 V between the R terminal and the other terminals on a thermostat subbase when the thermostat is not calling?
A) The meter is reading voltage that is left in the thermostat wire from the previous operating cycle. B) The common side of 24 V is supplied through the coils of the devices that are not operating. C) Thermostats are wired with both sides of 24 V. One side is supplied to the R terminal and the other to all the remaining terminals. D) Thermostats have battery backup, which can be read between R and the other terminals when the thermostat is not calling.
N-type silicon material is made with material from ___________
a. Family 3 elements. b. Family 4 elements. c. Family 5 elements.
As the evaporator load increases, an automatic expansion valve will ____________________ to reduce the evaporator pressure while a thermostatic expansion valve will ____________________ to reduce the evaporator superheat.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).