Which of the following is closest in mass to a white dwarf?
A) the Sun B) the Moon C) the Earth D) Jupiter
A
You might also like to view...
Might changes in the Sun affect weather or climate on Earth?
What will be an ideal response?
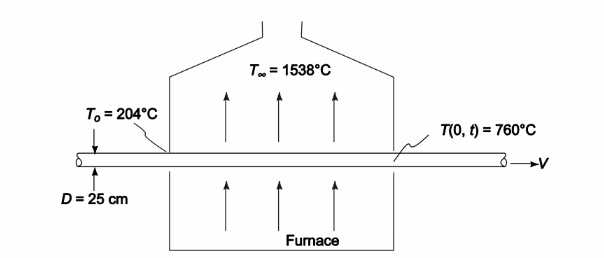
A mild-steel cylindrical billet, 25-cm in diameter, is to be raised to a minimum temperature of 760°C by passing it through a 6-m-long strip type furnace. If the furnace gases are at 1538°C and the overall heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the billet is 68 W/(m2 K), determine the maximum speed at which a continuous billet entering at 204°C can travel through the furnace.
GIVEN
• A mild-steel cylindrical billet is passed through a furnace
• Diameter of billet = 25 cm = 0.25 m
• Billet is to be raised to a minimum temperature of 760°C
• Length of furnace = 6 m
• Temperature of furnace gases (T?) = 1538°C
• The overall heat transfer coefficient h c= 68 W/(m2 K)
• Initial temperature of billet (To) = 204°C
FIND
• The maximum speed at which a continuous billet can travel through the furnace
ASSUMPTIONS
• The heat transfer coefficient is constant
• Billet is 1% carbon steel
• Radial conduction only in the billet, neglect axial conduction
SKETCH
The photo shows a galaxy known as Arp 220, and the inset shows this galaxy's spectrum. What can you infer?
A) Most of the light from this galaxy is infrared, indicating active star formation. B) Most of the light from this galaxy is visible light, and it comes from an active galactic nucleus. C) The broad peak is a spectral line indicating the presence of massive amounts of hydrogen gas. D) The spectrum peaks in the infrared, indicating that this galaxy has a huge redshift and must be far away.
The Earth cannot contain a giant permanent magnet because
A) the Earth doesn't have enough iron. B) the core would repel it. C) the Earth isn't large enough. D) ferromagnetism disappears at high temperature. E) its magnetic field is too large.