At a perfectly competitive firm, all of the following is true of the MRP curve EXCEPT
A) the MRP curve is the derived supply of labor.
B) the MRP curve shifts leftward when labor productivity falls.
C) the MRP curve shifts rightward when the product price rises.
D) the MRP curve shifts leftward when the demand for the final product falls.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is not appropriate, if we live in a world of fixed exchange rates?
A) monetary approach to the exchange rate B) elasticities approach C) monetary approach to the BOP D) absorption approach
If you're interested in deriving national income, add up
a. compensation for employees, interest, rent, corporate profit, and proprietors' income b. compensation for employees, interest, rent, corporate profit, and transfer payments c. compensation for employees, interest, rent, proprietors' income, and indirect business taxes d. compensation for employees, interest, rent, corporate profits, and capital depreciation e. compensation for employees, rent, corporate profits, proprietors' income, and transfer payments
Aggregate demand refers to the relationship between:
A. prices and the quantity of a good supplied. B. the price level and the quantity of real GDP supplied. C. prices and the quantity of a good demanded. D. the price level and the quantity of real GDP demanded.
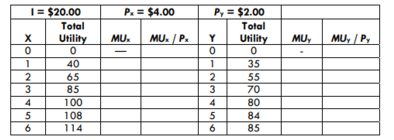
Refer to the table below. As stated in the first row, the income of the consumer (1) equals $20. The price of good X (Px) equals $3.00, and the price of good Y (Py) equals $2.00. Total utility derived from consuming X and Y is listed. What combination of goods X and Y will maximize utility subject to the consumer's budget constraint?