The radius of a star is 6.95 × 108 m, and its rate of radiation has been measured to be 5.32 × 1026 W. Assuming that it is a perfect emitter, what is the temperature of the surface of this star? (? = 5.67 × 10-8 W/m2 ? K4)
A) 6.27 × 103 K
B) 8.25 × 103 K
C) 8.87 × 103 K
D) 3.93 × 107 K
E) 5.78 × 107 K
A
You might also like to view...
Energy Conservation With Conservative Forces: A stone is released from rest at a height h at the left side of a loop-the-loop, as shown in the figure. There is no appreciable friction from the track or from air resistance. If the radius of the loop is R, what is the minimum height h for which the stone will not fall off the track at the top of the loop?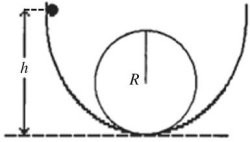
A. 3.5 R
B. 2.5 R
C. 2.0 R
D. 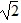 R
R
E. 3.0 R
A 3.00-kg stone is dropped from a 39.2 m high building. When the stone has fallen 19.6 m, the magnitude of the impulse the Earth has received from the gravitational force exerted by the stone is
A.
 s.
s.B.
 s.
s.C.
 s.
s.D.
 s.
s.E.
 s.
s.A superconductor expels any magnetic field from its interior. This is called
a. electromagnetic induction. b. Maxwell's effect. c. magnetic declination. d. the Meissner effect. e. none of the above.
Two capacitors with capacitances of 1.0 mC and 0.50 mF, respectively, are connected in series. The system is connected to a 150 V battery. What charge accumulates on the 1.0-mF capacitor?
a. 50 mC c. 100 mC b. 150 mC d. 33 mC