The graph below was generated by students in a physiology lab. The top trace (myogram) shows contraction force, the bottom (EMG) shows the electrical stimulus. On the graph, label a muscle twitch. What property of muscle is being tested here? What caused the increase in force (and subsequent decrease)?
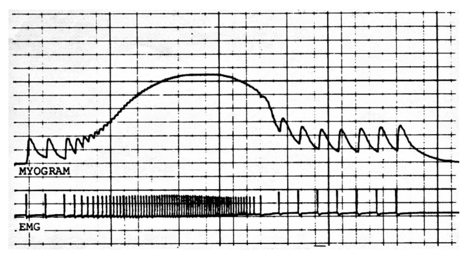
The clearest single twitches are the first few and last few peaks on the myogram. The muscle is being stimulated at an increasing rate (frequency), as evidenced by the decreasing time between subsequent stimulus pulses. This caused fusion of the twitches (summation), producing partial then complete tetanus, as well as an increase in peak force produced. Though the stimulus is maintained, the peak force starts to fall as the muscle fatigues. The students then decreased the stimulus frequency, allowing recovery from fatigue.
You might also like to view...
As a rule, during adulthood
A) all of the above. B) the skin becomes less elastic. C) the circulatory system becomes less efficient. D) skeletal muscles tend to lose strength.
Male ejaculation occurs as powerful, rhythmic contractions appear in which of the following muscles?
A) erector spinae and ischiocavernosus B) bulbospongiosus and internal oblique C) internal oblique and erector spinae D) ischiocavernosus and internal oblique E) ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus
Which of the following occurs during the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle?
A. Several follicles are developing an antrum B. The corpus luteum is shrinking C. The oocyte completes meiosis II D. The corpus luteum is enlarging E. Oogonia are transforming into primary oocytes
In what form is the body's largest pool of calcium?
A. embedded in collagen in many types of connective tissue B. blood, dissolved within the plasma C. skeletal muscle, stored in terminal cisternae D. bones, in the form of hydroxyapatites E. liver, inside the endoplasmic reticulum