Lee and Cody are playing a game in which Lee has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Lee has chosen either aggression or cooperation, Cody, who can see what Lee has chosen, must choose either aggression or cooperation at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 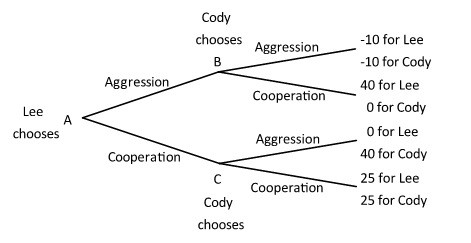 Suppose Lee and Cody enter into a binding non-aggression agreement. As part of that agreement, they negotiate a fine that Cody would have to pay to Lee if Cody chooses aggression after Lee chooses cooperation. For the fine to be effective, it would have to be:
Suppose Lee and Cody enter into a binding non-aggression agreement. As part of that agreement, they negotiate a fine that Cody would have to pay to Lee if Cody chooses aggression after Lee chooses cooperation. For the fine to be effective, it would have to be:
A. less than 15.
B. equal to 40.
C. equal to 25.
D. at least 15.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Compared with fiscal policy, monetary policy is:
a. more depenent on congressional actions b. quicker and easier to implement c. slower and more cumbersome to implement d. more likely to produce an offsetting net export effect
Suppose the production function for T-shirts can be represented as q = L0.25K0.75. Show that the marginal productivity of labor diminishes in the short run
What will be an ideal response?
Suppose a firm wants to build a new factory that would add pollution to an already polluted area. Under an offset program, the firm must:
a. install scrubbers and other government-mandated equipment. b. purchase pollution permits from the government. c. reduce or eliminate an old pollution source in the area. d. pay a tax which depends on the amount of pollution created.
Which is the following is true of games, in interactions between oligopolists? a. All games are cooperative in nature
b. Those in cooperative games are assumed to act independently. c. Communication is an important facet of noncooperative games. d. Most games are noncooperative games.