With real-world examples, explain the various factors that can cause a shift in the supply curve of a commodity
What will be an ideal response?
The supply curve of a commodity can shift for the following reasons.
a) The price of inputs used to produce the good: The price of inputs plays an important role in a producer's decision of how much of a good to supply. For example, a fall in the price of plastic is likely to increase the supply of plastic cups, at every price level.
b) The technology used to produce the good: Technology plays an important role in determining supply. If a new innovation increases labor productivity, it is likely that firms will start supplying more. For example, a new method of manufacturing cars can increase the number of cars supplied to the market at every price level.
c) The number and scale of sellers: The number and scale of sellers also determines the market supply. For example, if new firms enter the market for cigarettes, the supply of cigarettes will increase at every price level.
d) Expectations about the future: Expectations about the future greatly influence producers' decisions. For example, if producers of winter coats expect the next winter to be colder than normal, they will increase the production of winter coats.
You might also like to view...
"Throwing good money after bad" is also known as the _____ effect
a. anchoring b. sunk-cost c. status quo d. familiarity e. overconfidence
If a nation's real risk-free interest rate fell relative to foreign nations, it would cause the value of the domestic currency to _______ and net exports to ________ (fill in the missing blanks)
a. Fall; rise b. Fall, rise c. Remain unchanged; rise d. Rise; fall e. Remain unchanged; fall
Which of the following is an advantage of monetary policy?
A) It is faster to implement than fiscal policy. B) It acts more directly upon aggregate demand than fiscal policy. C) It is not subject to multiplier effects. D) It is unlikely to create inflation.
Refer to the graph shown for a small country that is a price taker internationally.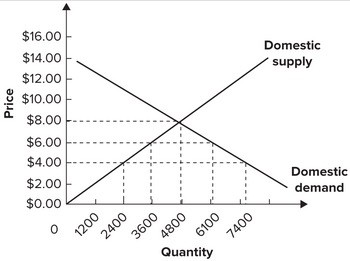 Assume the foreign supply of this product is perfectly elastic at a price of $4 per unit. Starting from a free trade equilibrium, a tariff in the amount of $2 per unit would be expected to cause domestic production to:
Assume the foreign supply of this product is perfectly elastic at a price of $4 per unit. Starting from a free trade equilibrium, a tariff in the amount of $2 per unit would be expected to cause domestic production to:
A. increase from 2,400 to 7,400. B. decrease from 7,400 to 6,100. C. increase from 2,400 to 3,600. D. decrease from 4,800 to 3,600.