There is often a trade-off between
A) productive efficiency and allocative efficiency.
B) limited and unlimited resources.
C) voluntary and involuntary exchanges.
D) economic efficiency and economic equity.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph for a competitive market for a product where the government has set a price floor of 0C to answer the question below. 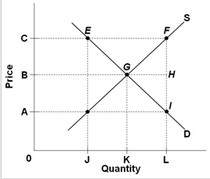 What quantity will the sellers be able to sell after the imposition of the price floor?
What quantity will the sellers be able to sell after the imposition of the price floor?
A. 0G B. CB C. 0F D. 0E
Which of the following is a predictable, secondary effect of a sharp increase in gasoline prices?
A) The federal government will place a quota on the number of fuel-efficient cars for sale, thus "forcing" consumers to purchase the gas guzzling vehicles. B) Producers will increase the production of fuel-efficient cars. C) the termination of research on the cost-effectiveness of alternative fuels to power automobiles. D) Producers will increase the production of gas guzzling vehicle
Exhibit 17-1: Global Comparison of Government Surpluses and Deficits as a Percentage of GDP, 2016 ? Country Surplus (+) or Deficit (-) as a percent of GDP Canada -1.10 Iceland 12.57 Latvia 0.06 Norway 3.99 Spain -4.51 United States -4.94? Given the information in Exhibit 17-1, which of the following statements is correct?
A. Canada was the closest of the countries shown to balancing its budget. B. Norway likely had to sell government securities to finance its overspending. C. Iceland experienced the largest deficit of the countries shown. D. The national debts of Canada, Spain and United States increased in 2016.
A country that has a capital account surplus:
A. is a net buyer of assets. B. has a current account surplus. C. will see its currency remain steady. D. is a net seller of assets.