Plane mirrors produce images which
A)
are always smaller than the actual object.
B)
are always larger than the actual object.
C)
are always the same size as the actual object.
D)
could be smaller or the same size as the actual object, depending on the placement of the object.
E)
could be larger or the same size as the actual object, depending on the placement of the object.
C
You might also like to view...
The hydrogen in our solar system was created from subatomic particles in
a. the Earth. b. our Sun. c. Jupiter. d. the big bang. e. supernovae.
The Chandra X-ray Observatory must operate in space because
A) x-rays do not penetrate Earth's atmosphere. B) x-rays are too dangerous to be allowed on the ground. C) x-ray telescopes require the use of grazing incidence mirrors. D) it was built by NASA.
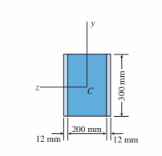
A composite beam is made up of a 200 mm 3 300 mm core (Ec 5 14 GPa) and an exterior cover sheet (300 mm 3 12 mm, Ee 5 100 GPa) on each side. Allowable stresses in core and exterior sheets are 9.5 MPa and 140 MPa, respectively. The ratio of the maximum permissible bending moment about the z axis to that about the y axis is most nearly:
(A) 0.5
(B) 0.7
(C) 1.2
(D) 1.5
What is the observational difference between Types I & II supernovae?
A: Ia's come from white dwarfs in binaries whereas II's come from dying massive stars B: I's are brighter than II's C: I's are fainter than II's D: I's are Hydrogen poor while II's are Hydrogen rich E: I's have no central remnant while II's have neutron stars