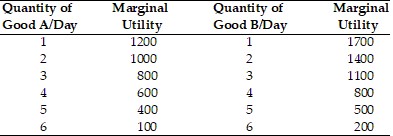
 Refer to the above table. If the price of Good A is $2, the price of Good B is $1, and the consumer has $9, the rational consumer will purchase
Refer to the above table. If the price of Good A is $2, the price of Good B is $1, and the consumer has $9, the rational consumer will purchase
A. 6 units of Good A and 3 units of Good B.
B. 5 units of Good A and 6 units of Good B.
C. 2 units of Good A and 5 units of Good B.
D. 6 units of Good A and 0 units of Good B.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Stagflation is a period of time when the economy is experiencing:
a. inflation and low unemployment. b. high unemployment and low levels of inflation at the same time. c. high inflation and high unemployment at the same time. d. low inflation and low unemployment at the same time.
The economic way of thinking is
a. a set of historical generalizations that indicates what goods should be produced. b. a body of statistical data that indicates how an economy should be organized. c. a set of basic concepts that helps one understand human choices. d. a set of complex, highly abstract theories that provides persons skilled in statistics with the information necessary to tell others what choices they should make.
A risk-neutral monopoly must set output before it knows the market price. There is a 50 percent chance the firm's demand curve will be P = 40 ? Q and a 50 percent chance it will be P = 60 ? Q. The marginal cost of the firm is MC = 3Q. What is the expression for the expected marginal revenue function?
A. E(MR) = 30 ? 2Q B. E(MR) = 50 ? 2Q C. E(MR) = 60 ? 2Q D. E(MR) = 40 ? 2Q
Firm 1 and firm 2 compete as a Cournot oligopoly. There is an increase in marginal cost for firm 1. Which of the following is NOT true?
A. Firm 1 will produce less. B. Both firm 1's and firm 2's reaction functions are shifted. C. Firm 2 will produce more. D. Profits of firm 1 will decrease.