The point in the phase diagram where the fusion curve, the vapor pressure curve, and the sublimation curve join is called the
A) critical point.
B) triple point.
C) melting point.
D) boiling point.
E) double point.
B
You might also like to view...
The chromosphere of the sun
a. is hotter than the photosphere. b. appears yellow-white in color during total solar eclipse. c. is the visible surface of the sun. d. produces an absorption spectrum. e. all of the above
A newly formed planet or large asteroid becomes molten due to
a. the last infalling objects. b. decay of radioactive element isotopes. c. the last infalling objects and decay of radioactive element isotopes. d. none of the other choices as newly formed planets remain solid inside.
A block lies on a horizontal frictionless surface. A horizontal force of 100 N is applied to the block giving rise to an acceleration of 3.0 m/s2
(a) Determine the mass of the block. (b) Calculate the distance the block will travel if the force is applied for 10 s. (c) Calculate the speed of the block after the force has been applied for 10 s. What will be an ideal response?
Atmospheric air at 10°C enters a 2 m long smooth rectangular duct with a 7.5 cm x 15 cm cross-section. The mass flow rate of the air is 0.1 kg/s. If the sides are at 150°C, estimate (a) the heat transfer coefficient, (b) the air outlet temperature, (c) the rate of heat transfer, and (d) the pressure drop.
GIVEN
Atmospheric air flow through a rectangular duct
Inlet bulk temperature (Tb,in) = 10°C
Duct length (L) = 2 m
Cross-section = 7.5 cm x 15 cm = 0.075 m ? 0.15 m
Mass flow rate (m) = 0.1 kg/s
Duct surface temperature (Ts) = 150°C
FIND
(a) The heat transfer coefficient ch
(b) The air outlet temperature (Tb,out)
(c) The rate of heat transfer (q)
(d) The pressure drop (?p)
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
The duct is smooth
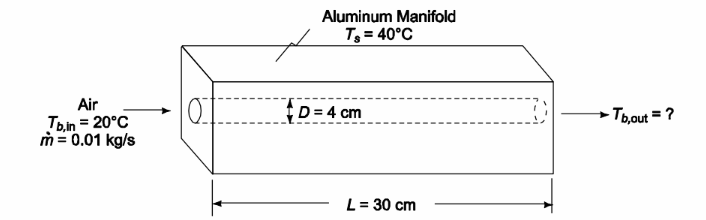
SKETCH
for dry air at the inlet bulk temperature of 20°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0251 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?) = 18,240 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
Specific heat (c) = 1012 J/(kg K)