Given: Small town with three transportation analysis zones, and origin-destination survey results. Provide a trip distribution calculation using the gravity model for two iterations; assume Kij = 1. The following table shows the number of productions and attractions in each zone:
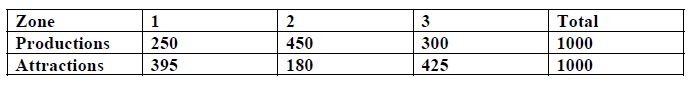
The survey’s results for the zones’ travel time in minutes were as follows:

The following table shows travel time versus friction factor.

What will be an ideal response?
The mathematical formulation for the gravity model as provided as Equation 12.3:
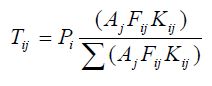
Since Kij = 1, this factor does not affect calculations. The iterative application of
Equation 12.3 is as follows:
Iteration 1
T11 = 250 × ((395 × 26) / ((395 × 26) + (180 × 41) + (425 × 52)))
T11 = 250 × (10,270 / 39,750)
T11 = 65
T12 = 250 × ((180 × 41) / ((395 × 26) + (180 × 41) + (425 × 52)))
T12 = 250 × (7,380 / 39,750)
T12 = 46
T13 = 250 × ((425 × 52) / ((395 × 26) + (180 × 41) + (425 × 52)))
T13 = 250 × (22,100 / 39,750)
T13 = 139
T21 = 450 × ((395 × 52) / ((395 × 52) + (180 × 13) + (425 × 50)))
T21 = 450 × (20,540 / 44,130)
T21 = 209
T22 = 450 × ((180 × 13) / ((395 × 52) + (180 × 13) + (425 × 50)))
T22 = 450 × (2,340 / 44,130)
T22 = 24
T23 = 450 × ((425 × 50) / ((395 × 52) + (180 × 13) + (425 × 50)))
T23 = 450 × (21,250 / 44,130)
T23 = 217
T31 = 300 × ((395 × 82) / ((395 × 82) + (180 × 50) + (425 × 39)))
T31 = 300 × (32,390 / 57,965)
T31 = 168
T32 = 300 × ((180 × 50) / ((395 × 82) + (180 × 50) + (425 × 39)))
T32 = 300 × (9,000 / 57,965)
T32 = 46
T33 = 300 × ((425 × 39) / ((395 × 82) + (180 × 50) + (425 × 39)))
T33 = 300 × (16,575 / 57,965)
T33 = 86
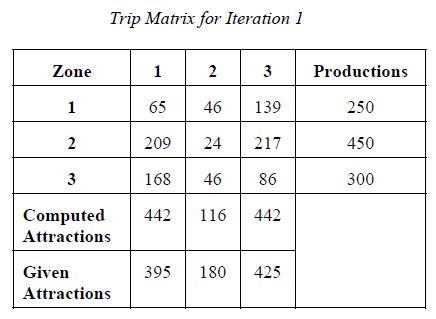
Next, calculate the adjusted attraction factors using Equation 12.4.
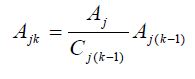
Zone 1
Ajk = (395 / 442) × 395
Ajk = 353
Zone 2
Ajk = (180 / 116) × 180
Ajk = 279
Zone 3
Ajk = (425 / 442) × 425
Ajk = 409
Now apply the gravity model formula for Iteration 2 using the above adjusted
attraction factors.
Iteration 2
T11 = 250 × ((353 × 26) / ((353 × 26) + (279 × 41) + (409 × 52)))
T11 = 250 × (9,178 / 41,885)
T11 = 55
T12 = 250 × ((279 × 41) / ((353 × 26) + (279 × 41) + (409 × 52)))
T12 = 250 × (11,439 / 41,885)
T12 = 68
T13 = 250 × ((409 × 52) / ((353 × 26) + (279 × 41) + (409 × 52)))
T13 = 250 × (21,268 / 41,885)
T13 = 127
T21 = 450 × ((353 × 52) / ((353 × 52) + (279 × 13) + (409 × 50)))
T21 = 450 × (18,356 / 42,433)
T21 = 195
T22 = 450 × ((279 × 13) / ((353 × 52) + (279 × 13) + (409 × 50)))
T22 = 450 × (3,627 / 42,433)
T22 = 38
T23 = 450 × ((409 × 50) / ((353 × 52) + (279 × 13) + (409 × 50)))
T23 = 450 × (20,450 / 42,433)
T23 = 217
T31 = 300 × ((353 × 82) / ((353 × 82) + (279 × 50) + (409 × 39)))
T31 = 300 × (28,946 / 58,847)
T31 = 148
T32 = 300 × ((279 × 50) / ((353 × 82) + (279 × 50) + (409 × 39)))
T32 = 300 × (13,950 / 58,847)
T32 = 71
T33 = 300 × ((409 × 39) / ((353 × 82) + (279 × 50) + (409 × 39)))
T33 = 300 × (15,951 / 58,847)
T33 = 81
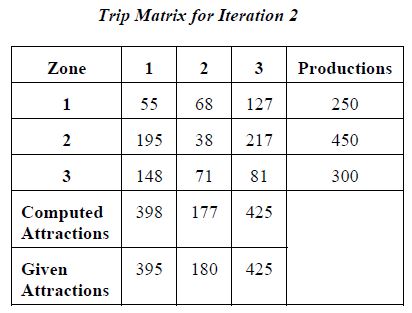
Observe that the computed attractions approximately equal the given attractions.
A total convergence would be expected in another iteration.
You might also like to view...
The dimensional requirement of foundations is partially based on which two factors?
a. square footage and weight of the building b. soil conditions and height of the building c. square footage of the building and soil conditions d. weight of the building and soil conditions
____________________ takes place at a temperature below 840°F.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
In one field trial comparing no-till and conventional tillage, soil samples taken after 15 years without liming revealed that the pH of the upper 15 cm was lower on the no-till plot than on the conventional plot. Which of the following most likely accounts for this difference?
A) earthworms were more active in the no-till plot B) acidifying effects of nitrogen-containing fertilizers C) organic decomposition produced more organic acids in the no-till plot D) plowing mixes the surface soil more thoroughly E) Al3+ ions are tied up by the organic matter thereby releasing H+ ions
To divide decimals, make the divisor a whole number by moving the decimal point all the way to the ____________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).