What is the opportunity cost of moving from point D to point C?
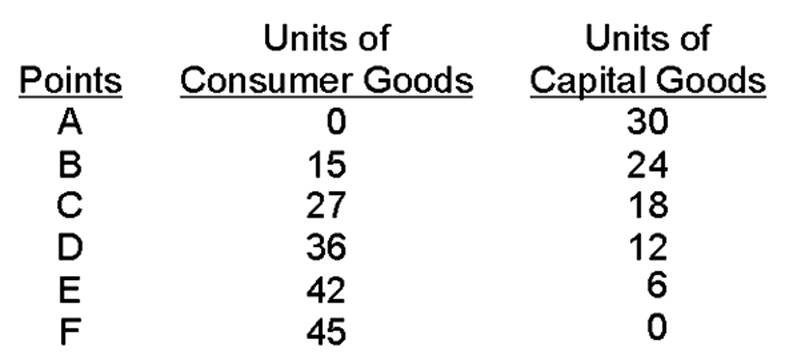
1 hamburger
You might also like to view...
Jonathan is currently enrolled in college full-time; however, he works part-time at a restaurant on weekends to earn some spending cash. Jonathan would be considered:
a) unemployed b) employed c) not in the labor force d) institutionalized
If there is an increase in the demand for U.S. automobiles, the
A) demand for dollars will fall. B) demand for dollars will rise. C) supply of dollars will fall. D) supply of dollars will rise.
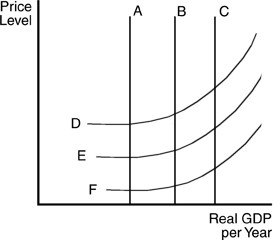 Refer to the above figure. Assume that B is the current long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve and that E is the current short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve. If a new discovery of large oil fields in Florida led to an increase in the nation's productive capacities, then we could expect the LRAS curve and the SRAS curve to
Refer to the above figure. Assume that B is the current long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve and that E is the current short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve. If a new discovery of large oil fields in Florida led to an increase in the nation's productive capacities, then we could expect the LRAS curve and the SRAS curve to
A. move to A and F. B. move to A and D. C. remain B and E. D. move to C and F.
A group price discriminator sells its product in Florida for three times the price it sets in New York. Assuming the firm faces the same constant marginal cost in each market and the price elasticity of demand in New York is -2.0, the demand in Florida
A) has an elasticity of -6.0. B) is more price elastic than the demand in New York. C) has an elasticity of -1.2. D) has an elasticity of -0.67.