The lifetime of a ?+ meson normally is 18 nanoseconds. In a large particle accelerator, scientists can create p+ mesons moving at speeds very close to the speed of light
What do the scientists observe when they measure the lifetime of a ?+ meson that is created at very high speed? A) The ?+ meson lasts 18 nanoseconds.
B) The ?+ meson lasts much less than 18 nanoseconds.
C) The ?+ meson lasts much more than 18 nanoseconds.
D) The ?+ meson no longer decays, and remains as a stable particle.
C
You might also like to view...
Helium has chemical properties similar to
A. hydrogen. B. lithium. C. neon. D. boron.
Three coplanar parallel straight wires carry equal currents I to the right as shown below. The current in the upper two wires is directed to the right, but the current in the bottom wire is directed to the left. Each pair of wires is a distance a apart. The direction of the magnetic force on the middle wire
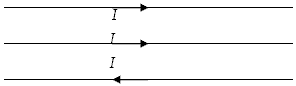
a.
is up out of the plane of the wires.
b.
is down into the plane of the wires.
c.
is in the plane of the wires, directed upwards.
d.
is in the plane of the wires, directed downwards
e.
cannot be defined, because there is no magnetic force on the middle wire.
Two ways that the temperature of a gas can be increased are by __________ and __________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Galileo's telescopic discovery of moons orbiting Jupiter was important because it showed that
a. the universe could contain centers of motion other than Earth. b. Earth might move along an orbit and not leave the Moon behind. c. Jupiter was much more massive than Earth. d. the universe could contain centers of motion other than Earth, Earth might move along an orbit and not leave the Moon behind, and Jupiter was much more massive than Earth. e. the universe could contain centers of motion other than Earth and Earth might move along an orbit and not leave the Moon behind.