Suppose we look at two distant galaxies: Galaxy 1 is twice as far away as Galaxy 2. In this case,
A) Galaxy 1 must be twice as big as Galaxy 2.
B) we are seeing Galaxy 1 as it looked at an earlier time in the history of the universe than Galaxy 2.
C) we are seeing Galaxy 1 as it looked at a later time in the history of the universe than Galaxy 2.
D) Galaxy 2 must be twice as old as Galaxy 1.
B
You might also like to view...
What was the purpose of the LCROSS mission?
a. To determine if lava still flowed beneath the crust b. To generate an altitude map of the Moon's surface c. To photograph geological features of the Moon d. To photograph geological features of the Moon e. To determine if there is water ice buried in soil of the Moon's south pole
Total Internal Reflection: A tank holds a layer of oil, of thickness To = 1.43 m, that floats on a layer of syrup of thickness Ts = 0.640 m, as shown in the figure. Both liquids are clear and do not mix together. A light ray, originating at the bottom of the tank at point P, crosses the oil-syrup interface at a point 0.900 m from the axis. The ray continues and arrives at the oil-air interface, 2.00 m to the right of P and at the critical angle. What is the index of refraction of the oil?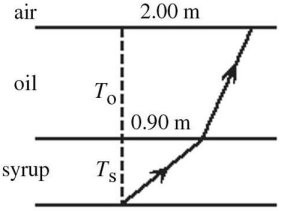
A. 1.64 B. 1.62 C. 1.60 D. 1.66 E. 1.68
Which of the following best defines lossless compression?
A. The degradation of image quality during compression. B. All image data is retained during compression. C. When a file size cannot be further reduced. D. Removing one color to create a transparency.
From shortest to longest wavelength, which of the following correctly orders the different categories of electromagnetic radiation?
A) infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays, radio B) radio, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays C) visible light, infrared, X-rays, ultraviolet, gamma rays, radio D) gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, radio E) gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, ultraviolet, infrared, radio