What are the signs of Q, W, and ?U for the process 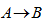 ?
?
A. 0, -, -
B. 0, +, +
C. +, -, 0
D. +, +, 0
E. -, +, 0
F. Other (specify)
F. Other (specify)
You might also like to view...
To reduce the carbon footprint of building energy consumption, photovoltaic (PV) cell panels are increasingly being used to provide a solar, self-sustaining source of electricity in both homes and large buildings. However, the semiconductor material that converts the solar light energy to electricity does not function efficiently at elevated temperatures, and the performance of a hot PV cell degrades. Externally mounted panels often rely for their cooling on atmospheric air. One such PV panel that has a square face (1 m * 1 m), as shown in the figure, is mounted on the side face of a building with air flowing over across it in parallel. If the maximum allowable temperature of the PV panel always has to be <= 70°C, calculate the rate of convection heat loss from the face of the panel when
air at 25°C flows over it with a velocity of 1.0 m/s. What is the heat loss if the wind speed decreased to 0.25 m/s? Also, do the results change significantly if the airstream is not parallel to the panel but has a pitch and yaw angle, relative to the panel alignment, or strikes it perpendicularly? Note that the heat loss in many ways, gives the PV panel designers an estimate of the typical range of electricity generation and the PV cell operating efficiency. GIVEN • Air flows over PV panel surface of 1m*1m in parallel • Air temperature (Ta) = 25°C • Air velocity (Us) = 1 m/s • Maximum allowable temperature of PV panel (Tw) = 70°C FIND • Rate of Convection heat loss when the velocity is 1 m/s. • Rate of heat loss when air velocity is reduced to 0.25 m/s • Change in results if airstream is not parallel but strikes at an angle perpendicularly? ASSUMPTIONS • Steady state PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0272 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 18.5 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At Tw: Prs = 0.71
Proportional Reasoning: Assuming equal rates of acceleration in both cases, how much longer would it take a car to stop if braking from 56 mi/h than from 28 mi/h?
A. 8 times as long B. 4 times as long C. 2 times as long D. 1.4 times as long E. the same in both cases
What type of spectrum is observed when the light from a hot, dense body is seen through a cooler, tenuous gas?
A. emission-line B. continuous C. absorption-line D. None of these choices are correct.
As you stand by the side of the road, a car approaches you at a constant speed, sounding its horn, and you hear a frequency of 80.0 Hz. After the car goes by, you hear a frequency of 60.0 Hz
What is the speed of the car? The speed of sound in the air is 343 m/s. A) 64.0 m/s B) 49.0 m/s C) 16.0 m/s D) 36.0 m/s E) 25.0 m/s