Oxygen is unloaded from the blood stream and diffuses into surrounding cells and tissues during ________
A) internal respiration
B) pulmonary ventilation
C) external respiration
D) respiratory gas transport
E) tidal volume
A
You might also like to view...
Serotonin
A. is a catecholamine neurotransmitter. B. acts as a neuromodulator. C. has an inhibitory effect on pathways that are involved in the control of muscles. D. has an excitatory effect on pathways that mediate sensations. E. is a neuropeptide.
Circular folds and intestinal villi
A) increase the surface area of the mucosa of the small intestine. B) carry products of digestion that will not pass through the walls of blood capillaries. C) produce new cells for the mucosa of the small intestine. D) secrete digestive enzymes. E) produce hormones.
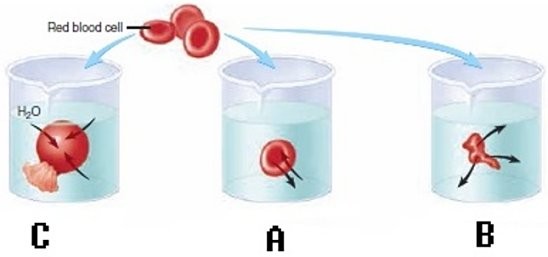 Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution "A" relative to the RBC?
Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution "A" relative to the RBC?
A. Isotonic solution B. Hypertonic solution C. Hypotonic solution
What structure carries deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta/mother?
A) Umbilical vein B) Ductus arteriosus C) Umbilical artery D) Foramen ovale