Refer to the table below. In moving from combination b to c, the consumer:
The table shows an indifference schedule for several combinations of X and Y.
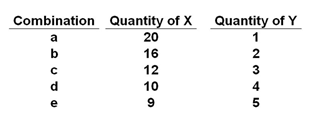
A. Gets 1 unit of X for 1 unit of Y
B. Gets 2 units of X for 2 units of Y
C. Gets 3 units of X for 1 unit of Y
D. Gives up 4 units of X for 1 unit of Y
D. Gives up 4 units of X for 1 unit of Y
You might also like to view...
The charitable organization Creating Hope International trains women in Afghanistan to become tailors. This effort reduces
A) entrepreneurship differences between advanced and developing economies. B) human capital differences between advanced and developing economies. C) physical capital differences between advanced and developing economies. D) agricultural differences between advanced and developing economies. E) manufacturing differences between advanced and developing economies.
Rapid growth of the money supply might seem appropriate to ________ economists, because ________
A) Keynesian; it can hasten the economy's return to a long-run equilibrium B) Keynesian; the resulting inflation will have no effect on real output C) classical; stabilizing fluctuations contributes to long-run growth D) classical; it will make prices more flexible E) none of the above
The fact that indifference curves are bowed in toward the origin
A) is not true. B) follows from the fact that more is preferred to less. C) follows from the property that the consumer likes diversity in his or her consumption bundle. D) follows from the property that consumption and leisure are normal goods.
Which of the following can help shape the incentive structure of the country of Gammaland?
a. resource availability b. prices c. income d. incentives e. All of the answers are correct