Which of the following changes would not lead to a shift in Canada's production possibilities curve?
a. the introduction and use in Canada of more advanced technology
b. a substantial emigration of Canadian workers to the U.S.
c. a prolonged summer drought in Canada's Prairie Provinces that destroys 18% of Canada's wheat harvest
d. a sharp increase in the number of Canadians earning advanced degrees in education, e.g., BA's, BS's, MD's and PhD's
e. a change in the composition of Canada's output
E
You might also like to view...
Suppose an individual has a fixed amount of wealth to allocate between consumption in two periods (C1 and C2). Any funds not spent in period 1 will earn interest (at the rate r), which will increase purchasing power in period 2 . Consider four possible reactions to an increase in r: I. C1 increases. II. C1 decreases. III. C2 increases. IV. C2 decreases. Which of these is consistent with the
hypothesis that both C1 and C2 are normal goods? a. I, II, III, and IV. b. I, II, and IV, but not III. c. I, III, and IV, but not II. d. II and III, but not I and IV. e. I, II and III, but not IV.
The MFC curve increases for a monopsonist because:
a. hiring more workers raises total labor costs. b. output price rises as a firm's market power increases. c. hiring more workers does not affect wages. d. the later workers hired are less productive. e. as more workers are hired, all workers receive higher wages.
Since 1953 the United States has imposed a quota to limit the imports of peanuts. Figure 9-3 illustrates the impact of the quota. Refer to Figure 9-3. What is the area that represents the deadweight loss as a result of the quota?
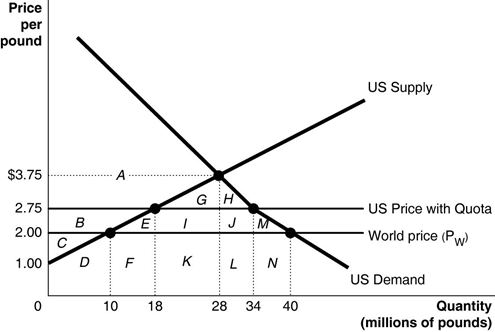
A) G + H
B) G + H + I + J
C) E + I + J + M
D) E + M
If a currency depreciates, a country’s net exports
A. fall and AD increases. B. rise and AD increases. C. fall and AD decreases. D. rise and AD decreases.