In equilibrium, the price of a transferable emissions permit
A) is constrained to the amount the government first charged for it.
B) equals the marginal cost of abatement for all firms.
C) equals the marginal cost of abatement for the firm with the highest cost, and exceeds the marginal cost of abatement of other firms.
D) equals the marginal cost of abatement for the firm with the lowest cost, and is less than the marginal cost of abatement of other firms.
E) equals the marginal social cost of emissions.
B
You might also like to view...
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.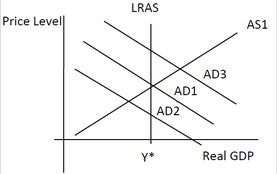 Assume the economy is initially at the full employment level of real GDP. A decrease in net exports will ________.
Assume the economy is initially at the full employment level of real GDP. A decrease in net exports will ________.
A. reduce the full employment level of real GDP B. reduce output in the economy C. raise the price level D. reduce the unemployment rate
According to the natural rate hypothesis, in the short run an increase in the inflation rate brings
A) an increase in the natural unemployment rate. B) an increase in the unemployment rate. C) no change in the unemployment rate. D) a decrease in the unemployment rate. E) a decrease in the natural unemployment rate.
If a monopolistically competitive firm raises its price,
a. quantity demanded falls to zero b. quantity demanded declines, but not to zero c. the market supply curve shifts outward d. the market supply curve shifts inward e. quantity demanded remains constant
In the short run, with predetermined prices, when output is greater than planned aggregate expenditure, firms will:
A. increase planned aggregate expenditure. B. increase production. C. decrease planned aggregate expenditure. D. reduce production.