An increase in the expected future price of a good will cause the current demand for the good to:
a. decrease, which is a shift to the left of the demand curve.
b. decrease, which is a shift to the right of the demand curve.
c. increase, which is a shift to the left of the demand curve.
d. increase, which is a shift to the right of the demand curve.
d
You might also like to view...
Real business cycle theory explains changes in employment and output by focusing on
A) changes in fiscal policy. B) real supply-side factors. C) the interaction of fiscal and monetary policies. D) changes in monetary policy.
Assume that foreign capital flows from a nation increase due to political uncertainly and increased risk. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and current international transactions balance in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. The GDP Price Index falls and current international transactions
balance becomes more positive (or less negative). b. The GDP Price Index rises and current international transactions balance becomes more negative (or less positive). c. The GDP Price Index and current international transactions balance remain the same. d. The GDP Price Index rises and current international transactions balance remains the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 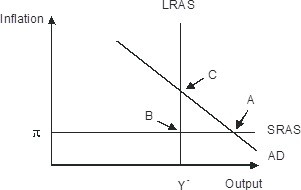
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A
You participate in a taste test for a new protein supplement called "Kapow." You are given five consecutive one ounce vials of the supplement and after consuming each vial you are asked to note your reaction. You consume the first vial and your response
is: "Hmmm, quite good!" After the second, you say, "Not bad at all." After the third, you note, "It's alright." and after the fourth you wince, "No more, the after-taste is getting to me. I need water." What economic principle does this scenario illustrate? Define the principle. What will be an ideal response?