Antihistamines relieve allergy symptoms by
a. inhibiting the release of histamines and
cytokines.
b. binding directly to histamines.
c. destroying mast cells before they can
produce histamines.
d. binding to the allergens.
e. stimulating effector T cells to produce more
cytokines
A
You might also like to view...
Prior to the Mesozoic Era, the primary photosynthesizers in the ocean were the cyanobacteria and the diatoms
A. true B. false
What would be the result of a mutation that reduces the amount of acrosomal enzymes?
A. Male infertility due to inability of the sperm to tunnel through the blastula. B. Male infertility due to inability of the sperm to tunnel through the zona pellucida. C. Female infertility due to blockage of sperm from tunneling through the allantois. D. Female infertility due to blockage of sperm from tunneling through the archenteron. Clarify Question What is the key concept addressed by the question? What type of thinking is required? Gather Content What do you already know about the acrosomal region? What other information is related to the question? Choose Answer Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer? Reflect on Process Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
If the mean annual precipitation of a region, currently characterized by grasslands, was to increase by 50 cm. per year, what type of biome(s) would evolve in that region?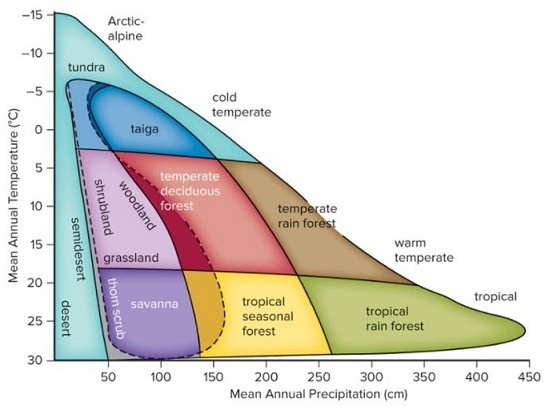
A. taiga and temperate rain forests B. savanna C. deserts and tropical rain forests D. temperate forests E. temperate forests and shrublands
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor limit an enzyme's activity?
A. A noncompetitive inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme. B. A noncompetitive inhibitor binds to the substrate, preventing it from binding to the enzyme. C. A noncompetitive inhibitor binds to a coenzyme or cofactor, preventing it from binding to the enzyme. D. A noncompetitive inhibitor binds to an allosteric site of the enzyme.