Where does translation take place in a typical eukaryotic cell?
a. the nucleus
b. ribosomes
c. the cytoplasm
d. ribosomes and the cytoplasm
D
You might also like to view...
The division of a bacterial cell occurs as the:
A. cell wall develops cracks around the equator of the cell. B. chromosomes are pulled toward the ends of the cell. C. actin and microtubules constrict the cytoplasm. D. new membrane and cell wall materials begin to grow and form a septum.
When a population is small relative to its carrying capacity, its growth will be:
A. geometric. B. exponential. C. logistic. D. both geometric and exponential. E. both geometric and logistic.
In Cell 1,
Consider the following plant cells floating in an open beaker containing 0.2M sucrose. By definition, an open beaker has a pressure potential 0 MPa. Assume that the cells have come to equilibrium with the solution in the beaker.
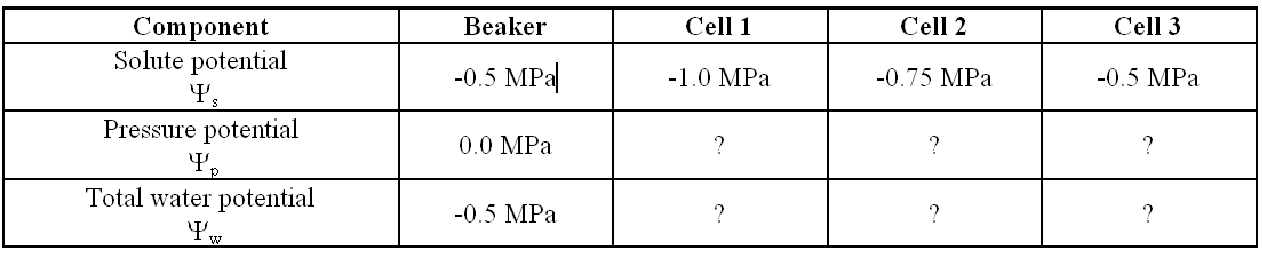
A. ?p = 0.0 MPa and ?w = 0.0 MPa.
B. ?p = 0.0 MPa and ?w = -1.0 MPa.
C. ?p = +0.5 MPa and ?w = -0.5 MPa.
D. ?p = -0.5 MPa and ?w = -0.5 MPa.
E. ?p = 0.0 MPa and ?w = +0.5 MPa.
Clarify Question
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
Gather Content
What do you already know about water potential? How does it relate to the question?
Consider Possibilities
What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Some components and breakdown products of commonly used pesticides are intercalating agents, which cause mutations by _____
1.their incorporation into the DNA molecule due to structural resemblance to bases 2.chemically modifying the bases in DNA 3.inserting themselves into the double helix of DNA and causing errors during replication 4.generating free radicals that produce mutations if they interact with DNA