An economist might say that people choose not to get a college degree because they may have to borrow money to go to college, and the interest they have to pay on that loan in the future will affect their decisions today. This is an example of which kind of statement?
a. positive statement
b. normative statement
c. trade-off statement
d. allocative statement
a. positive statement
You might also like to view...
If prices of both horizontal and vertical goods decrease by 50%,
A) budget constraint will be unchanged. B) slope of the budget constraint will increase. C) slope of the budget constraint will decrease. D) budget constraint will shift outward in a parallel fashion.
"Near monies" are: a. included in the M1 definition of the money supply
b. highly liquid assets that are close substitutes for money. c. stocks, bonds, and real estate. d. U.S. notes and Federal Reserve notes.
Figure 5-2
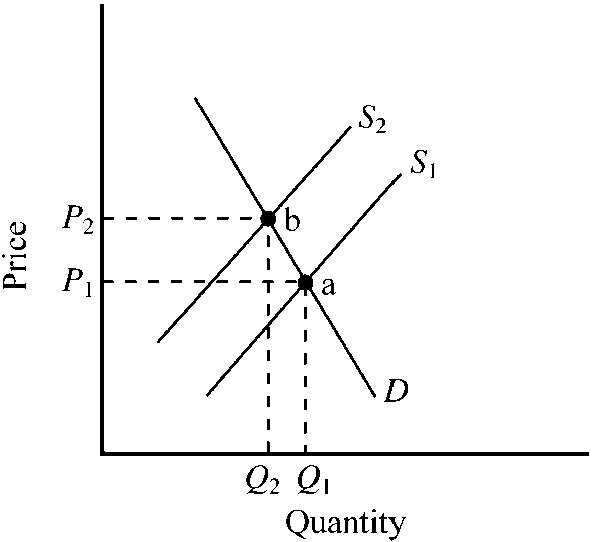
illustrates the market for a product that generates an external cost. S1 is the private market supply curve, while S2 is the supply curve including the external cost. Which of the following is true?
a.
Point a illustrates the competitive private market outcome, while point b illustrates the outcome consistent with economic efficiency.
b.
Point b illustrates the competitive private market outcome, while point a illustrates the outcome consistent with economic efficiency.
c.
The competitive private market outcome is consistent with the conditions for economic efficiency.
d.
The good will tend to be undersupplied relative to the conditions for economic efficiency.
If a government wishes to limit or prohibit fluctuations in exchange rates, it will choose:
a. to fix, or peg, the value of its currency to some base currency over a sustained period. b. to allow its currency to rise or fall in price, depending on a variety of supply and demand factors. c. to suspend purchases and sales of its currency. d. to allow the rate to be set by international banks.