How can corporate management defend itself against a hostile takeover attempt?
There are three strategies management can use to defend itself against a hostile takeover attempt. First, it
can use the corporation's profits to buy its own stock, rather than to pay dividends to stockholders, until the
corporation virtually owns itself. This makes it impossible to take over. Second, it can make itself less
attractive by borrowing heavily and paying a one-time cash dividend to its own stockholders. Third, it can
encourage a friendly corporation to attempt a takeover, under which the threatened management may be
able to survive.
You might also like to view...
Legal restrictions on competition, such as the grant of patent privileges to inventors,
A) destroy property rights. B) expand property rights. C) both destroy and expand property rights. D) neither destroy nor expand property rights because patents are granted by the U.S. Constitution.
The perfectly competitive firm's demand curve has
A) a negative slope. B) a positive slope. C) an undefined slope. D) a slope of 0.
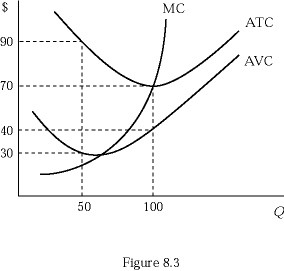 Figure 8.3 shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost curves. At Q = 50, the average fixed cost is:
Figure 8.3 shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost curves. At Q = 50, the average fixed cost is:
A. $30. B. $40. C. $50. D. $60.
The labor supply curve for a monopsony is
A) perfectly horizontal. B) perfectly vertical. C) upward sloping but not perfectly vertical. D) downward sloping.