Dr. X, an assistant professor at a large state university, is trying to decide how to allocate the 50 hours a week she spends working among the various activities expected of an assistant professor. The professor wants to maximize her raise next year and the table shows estimates of how time spent in each activity will contribute to her raise: 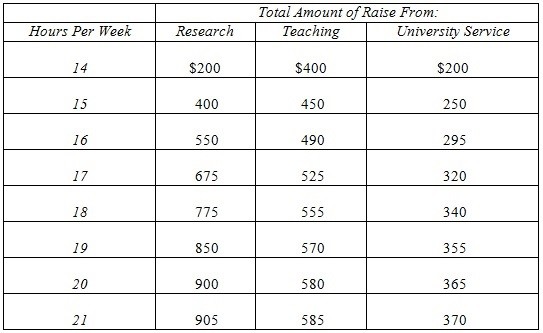 Given the above information, if she decides that she will work 54 hours a week instead, how should she allocate her time?
Given the above information, if she decides that she will work 54 hours a week instead, how should she allocate her time?
A. 20 hours research, 18 hours teaching, 16 hours service
B. 21 hours research, 19 hours teaching, 14 hours service
C. 20 hours research, 17 hours teaching, 17 hours service
D. 18 hours research, 18 hours teaching, 18 hours service
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Gross domestic product minus
a. net domestic product equals national income b. depreciation equals net domestic product c. indirect business taxes equals national income d. gross domestic product equals personal income e. net domestic product equals gross domestic product
Probably the simplest approach to the problem of oligopolistic interdependence is to
A. conduct market experiments. B. assume that rivals will pursue a course most detrimental to the firm concerned. C. ignore the actions of rivals. D. increase the firm’s advertising outlay considerably.
If a price ceiling is set at $10, and the equilibrium market price is $8, then which of the prices below is the price that consumers actually pay?
a. $2 b. $10 c. $8 d. $18
The creation of savings plans such as savings deposits and money market mutual accounts that allow easy transfer of funds between interest-earning assets and checkable deposits tends to
A) lower the cost of holding money. B) reduce the demand for money. C) increase the demand for money. D) increase the risk of holding money.