Based on your understanding of the Phillips curve, explain what happens to actual inflation (relative to expected inflation) when the actual unemployment rate is either above or below the natural rate of unemployment
What will be an ideal response?
When the actual unemployment rate is equal to the natural rate of unemployment, we know that actual inflation and expected inflation must be equal. In such a case, all else fixed, inflation will not change. If the actual unemployment rate were to fall below the natural rate, inflation would increase. So, the natural rate of unemployment rate may also be referred to the non-accelerating-inflation rate of unemployment. If the opposite occurs, inflation will fall below expected.
You might also like to view...
What is a balance of payments system, and what three types of international transactions are typically found in the balance of payments?
What will be an ideal response?
When the Fed buys bonds on a mass scale
A) bonds go to the Fed, and dollars go into the banking system, so the money supply tends to rise. B) bonds go to the Fed, and dollars exit the banking system, so the money supply tends to fall. C) banks have more bonds and fewer dollars, so the money supply tends to fall. D) banks have more bonds and fewer dollars, so the money supply tends to rise.
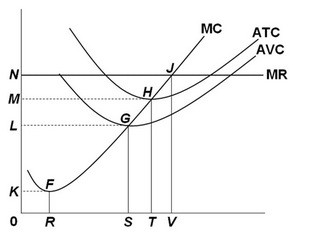 Given the above graph, the competitive firm's short-run supply curve is the:
Given the above graph, the competitive firm's short-run supply curve is the:
A. MC curve above F. B. MC curve above J. C. MC curve above G. D. MC curve above H.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as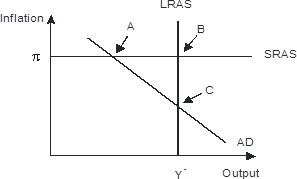
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward