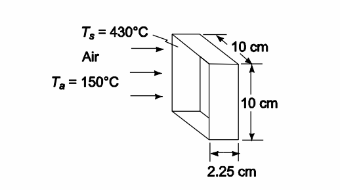
Air at an average temperature of 150°C flows through a short square duct 10 × 10 × 2.25 cm at a rate of 15 kg/h. The duct wall temperature is 430°C. Determine the average heat transfer coefficient, using the duct equation with appropriate L/D correction. Compare your results with flow-over-flat-plate relations.
GIVEN
• Air flowing through a short square duct
• Average air temperature (Ta) = 150°C
• Duct dimensions = 10 × 10 × 2.25 cm = 0.1 × 0.1× 0.0225 m
• Duct wall surface temperature (Ts) = 430°C
• Mass flow rate (m ) = 15 kg/h
FIND
The average heat transfer coefficient ( h c) using (a) The duct equation with appropriate L/D correction (b) The flow-over-flat-plate relation
ASSUMPTIONS
• Constant and uniform duct wall temperature
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average temperature of 150°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0339 W/(m K)
Absolute viscosity (?b) = 23.683 × 10–6 (Ns)/m2
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At the surface temperature of 430°C,
the absolute viscosity (?s) = 33.66 × 10–6
The hydraulic diameter of the duct is
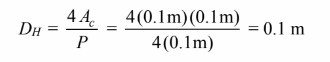
The Reynolds number is
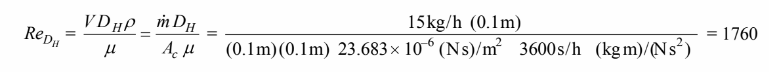
Therefore, the flow is laminar.
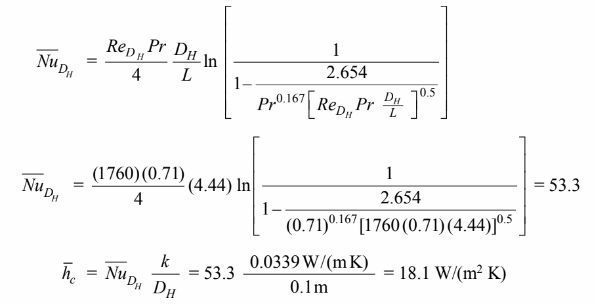
(a) Using the Hausen correlation, Equation (7.41) to estimate the Reynolds number with
D/L = DH/L = 10/2.25 = 4.44
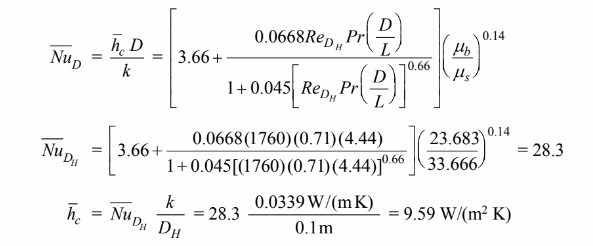
(b) Applying the flow-over-flat-plate relation of
You might also like to view...
The strong tendency of certain minerals to break along smooth, parallel planes is known as ________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Which of the following polymer combinations is least likely to mix?
(a) Liquids of two different long-chain molecules with a positive enthalpy of mixing. (b) A liquid solvent and solid polymer with solubility parameters of 19 MPa0.5 and 20 MPa0.5, respectively. (c) Liquids of two different long-chain molecules with a negative enthalpy of mixing. (d) Liquids of two different short molecules with a positive enthalpy of mixing.
An electron moving from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a 12. volt battery gains (or loses) how much energy? (Be sure to indicate whether it is a gain or loss.)
What will be an ideal response?
A skater rotates quickly on the ice. He pushes his arms out. What happens to his rotational kinetic energy?
1.It increases. 2.It decreases. 3.It stays the same. 4.It is impossible to determine.