Consider that in Country A, there are some models of cars available in the luxury segment produced by the domestic companies. Some more models are available in the same segment in Country B as well. Explain, with the help of suitable figures, how the consumers in both countries gain if they engage in free trade.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: Let's assume that in the pre-trade situation, car producers in Country A sold 16 luxury segment car models in the domestic market and producers in Country B sold 20 car models in the domestic market.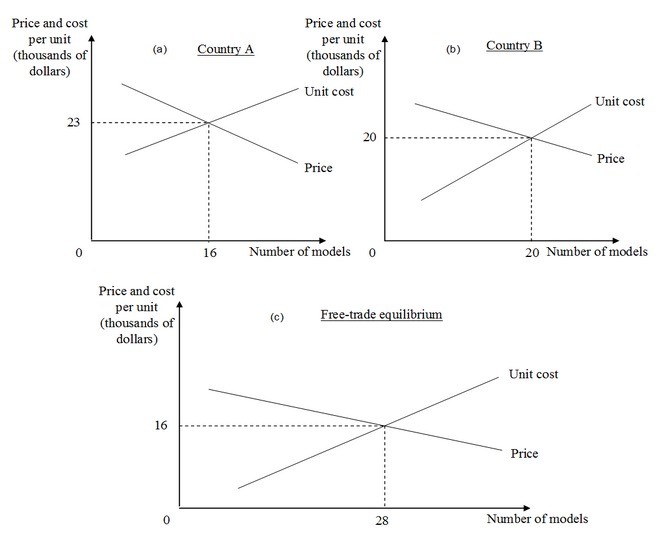
In the absence of trade, each country must produce the luxury cars it consumes, and the number of models is limited by the size of each domestic market. From the figures illustrating no-trade equilibrium in Country A, (Figure a), and Country B (Figure b), we see that 16 models were being sold in Country A at a price of $23,000 per car and in Country B 20 models were sold at $20,000 per car.
Free trade allows expansion of the market for the manufacturers in both countries. The combined unit cost curve also changes as shown in Figure c. Here, the "free-trade" situation allows consumers in both countries to have access to 28 models, and the price per car declines to $16,000. For each of the countries, some of these 28 models will be produced locally, and some will be imported. Also, some of the countries' production of their models will be exported. We also note that, in the transition from "no-trade" to "free-trade," some models (those that are more adversely affected by increasing import competition and those that are not demanded by foreign buyers) will disappear due to weak sales. However, the net change in welfare will be positive.
Consumers in each country gain since they have access to more models in total than they would with "no trade," and the price per car decreases.
You might also like to view...
Consumers eat salsa with taco chips. The price of salsa rises. How does the increase in the price of salsa affect the demand for taco chips?
A) It decreases the demand for taco chips. B) It increases the demand for taco chips. C) It has no effect on the demand for taco chips. D) It will decrease the demand for taco chips only if taco chips are a normal good. E) It could increase, decrease, or have no effect on the demand for taco chips, but more information is needed to determine the impact.
Which round of GATT led to the formation of the WTO?
What will be an ideal response?
The term "fine-tuning the economy" implies: a. making government economic policy more "people oriented"
b. using government policies to adjust the economy and promote economic stability. c. solving microeconomic problems such as externalities and losing sight of the big picture. d. placing fewer regulations on the private sector, thereby eliminating the need for government intervention. e. designing policies based exclusively on leading economic indicators.
Suppose Elroy's budget line is as shown on the diagram. If his tastes change in favor of Coke and against popcorn, the budget line will:
A. become steeper.
B. become flatter.
C. shift rightward.
D. be unaffected.