Assets minus liabilities equal:
A. current income minus spending on current needs.
B. wealth.
C. saving.
D. investment.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Brian is running for state senator and if elected, pledges to improve economic growth. His plan for economic growth includes increasing spending on public education and providing tax incentives to encourage improved private education
His plan is likely to A) slow economic growth because it includes a provision for private education. B) have no effect on economic growth because property rights are not changed. C) speed economic growth as the quality of resources improve. D) fail because the provision for private education limits government involvement in education. E) have no effect on economic growth because government spending cannot affect the economic growth rate.
which shows the production possibilities frontier for Good A and Good B. When moving from point g to point f, the production of _____
a. Good B increases without a change in the production of Good A. b. Good A increases without a change in the production of Good B. c. both Good A and Good B increases. d. Good B decreases but Good A does not increase as much as if resources were used more efficiently. e. Good B increases and the production of Good A decreases.
A firm should continue producing until
A. the cost of producing the output equals the revenues obtainable from selling the output. B. average costs are at a minimum. C. the average cost when another unit is produced equals the average revenue obtainable from selling the extra unit. D. the cost of increasing output by one more unit equals the revenues obtainable from selling the extra unit.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Below are cost curves for Dom's Barber Shop, a monopolistically competitive firm. 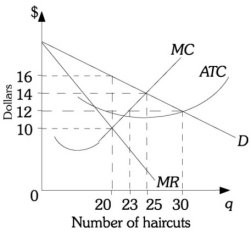 Figure 15.1 Refer to Figure 15.1. The profit-maximizing number of haircuts for Dom's Barber Shop is
Figure 15.1 Refer to Figure 15.1. The profit-maximizing number of haircuts for Dom's Barber Shop is
A. 20. B. 23. C. 25. D. 30.