For a given level of equilibrium GDP, a tight-money/easy-fiscal policy mix compared with easy-money/tight-fiscal policy mix implies a
A) lower interest rate.
B) lower level of investment.
C) higher level of taxation.
D) lower level of government expenditures.
B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a difference between the income effect and the substitution effect?
a. The income effect refers to the way a change in income alters the buying power of an individual, while the substitution effect occurs when a good becomes cheaper and people seek alternatives. b. The income effect refers to the way a change in price alters the buying power of an individual, while the substitution effect occurs when a good becomes expensive and people seek alternatives. c. The income effect refers to the way a change in price alters the buying power of an individual, while the substitution effect occurs when the opportunity cost of a good increases and people seek alternatives. d. The income effect occurs when a good becomes expensive and people seek alternatives, while the substitution effect refers to the way a change in income alters the buying power of an individual.
Why is private ownership an important source of economic prosperity?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the competitive market diagram for product Z. Assume that the current market demand and supply curves for Z are D 2 and S 2 . If there are substantial external costs associated with the production of Z, then:
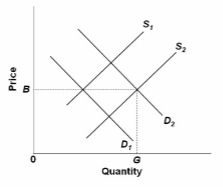
A. a price lower than B and an output greater than G would improve resource allocation.
B. government should levy a per-unit excise tax on Z to shift the demand curve to the right.
C. government should levy a per-unit excise tax on Z to shift the supply curve toward S 1 .
D. government should subsidize the production of Z to lower equilibrium price and increase
equilibrium output.
The aggregate supply-aggregate demand diagram relates various levels of
A. imports and exports of goods against exchange rates. B. all prices as measured by the CPI and production as measured by real GDP. C. the price and quantity of a particular good. D. production of two different goods.