Refer to the graph below representing the purely competitive market for a product. When the market is at equilibrium, the consumer surplus would be represented by the area:
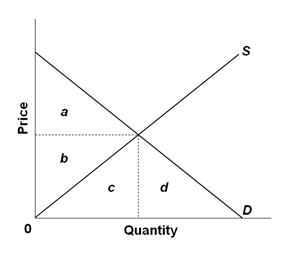
A. a + b + c + d
B. a + b + c
C. a
D. b + c
C. a
You might also like to view...
If prices are sticky
A) prices will quickly adjust to changes in demand. B) economic activity will not be coordinated efficiently. C) quantity supplied will always equal quantity demand. D) economic activity will be coordinated efficiently.
In the steady-state diagram of the Solow model, an increase in saving per worker is shown by
A) shifting the saving-per-worker curve down, resulting in a lower steady-state capital—labor ratio. B) shifting the saving-per-worker curve up, resulting in a higher steady-state-capital—labor ratio. C) shifting the saving-per-worker curve up, resulting in a lower steady-state capital—labor ratio. D) shifting the saving-per-worker curve down, resulting in a higher steady-state capital—labor ratio.
To sell more units, a monopolist
A) simply moves across its horizontal demand curve to a larger quantity. B) moves down its demand curve to a lower price that will increase quantity demand. C) can continue to receive the same price it always has as long as it has its customers' goodwill. D) must be willing to lower the barriers to entry that have protected it.
If an increase in consumer incomes leads to a decrease in the demand for camping equipment, then camping equipment is
a. a complementary good b. a substitute good c. a normal good d. an inferior good e. none of the above