Based on the demand curves for perfectly competitive firms and for monopolies, which action would be most likely to lower market price?
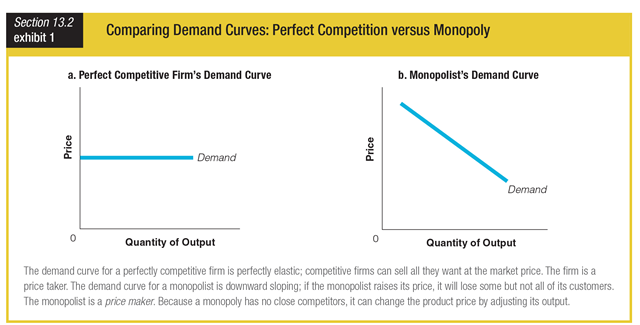
a. a perfectly competitive firm increasing production
b. a monopolist increasing production
c. a monopolist cutting production
d. a perfectly competitive firm cutting production
b. a monopolist increasing production
You might also like to view...
With respect to Friedman's natural rate theory, expansionary monetary policies can
a. move output above the natural rate but leave unemployment at the natural rate in the short-run. b. only affect inflation and not unemployment in the long-run. c. leave output at its natural rate with a simultaneous decrease in the natural rate of employment. d. move output and employment below the natural rate.
For which of the following reasons is VAT considered a very important revenue generator for a government?
a. It is regressive in nature b. It targets only individuals in the high income class c. It cannot be avoided by individuals d. It boosts a country's export e. It lowers a country's import
Refer to the diagrams below. In which of them would we see a shortage at the initial price after the indicated curve has shifted?
In the diagrams below, the subscript "1" refers to the initial position of the curve, while the subscript "2" refers to the final position after the curve shifts.
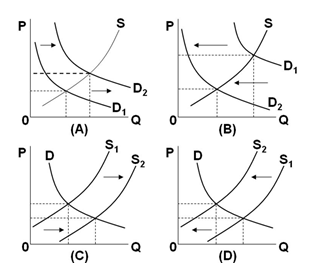
A. A and D
B. B and D
C. B and C
D. A and C
If the inverse demand function for a monopoly's product is p = a - bQ, then the firm's marginal revenue function is
A) a. B) a - (1/2)bQ. C) a - bQ. D) a - 2bQ.