If the price of chewing gum is represented by P in equation P = 25 - 0.5 QD, then the corresponding quantity of chewing gum demanded is represented by the demand equation
A) QD = 2P - 0.5. B) QD = 0.5P + 25. C) QD = -5 + 10P. D) QD = 50 -2P.
D
You might also like to view...
If the Fed increases the inflation rate in the short run before people's expected inflation changes, what occurs? What happens in the long run?
What will be an ideal response?
The productivity slowdown in the United States from 1973 to 1995
A. can be explained easily with economic theory. B. continued into the third millennium. C. still confuses economists. D. was a continuation of the slowdown from 1948 to 1973.
How would the real exchange rate need to change to get aggregate expenditure to increase?
A. Remain constant B. Increase C. Exchanges rates don't generally affect aggregate expenditure. D. Decrease
Refer to the diagram, in which solid arrows reflect real flows; broken arrows are monetary flows. Flow (2) might represent:
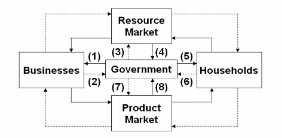
A. the provision of national defense by government.
B. a government subsidy to farmers.
C. corporate income tax payments.
D. welfare payments to low-income families.