Following the economic crisis in 1994-1995, the Mexican peso fell sharply in value. What will be the main economic effects in Mexico of such an exchange rate change?
a. It will decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply, so that output will certainly fall, and prices may fall as well.
b. It will increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply, so that output will certainly rise, and prices may rise as well.
c. It will increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply, so that prices will certainly rise and output may rise as well.
d. It will decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply, so that prices will certainly fall and output may fall as well.
c
You might also like to view...
An example of moral hazard is
a. A taxi driver paid per mile taking the shortest route b. a piece-rate garment worker shirking more than a per hour worker c. an hourly salesman working harder than a commission salesman d. an author on contract going to fewer book signings as one with a percentage royalty rate
The questions below are based on the table below. Fill in the blank spaces first. 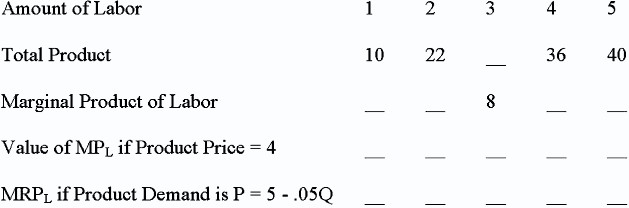 If the product market is perfect and the labor market is imperfect, what will be the wage rate paid to the laborer?
If the product market is perfect and the labor market is imperfect, what will be the wage rate paid to the laborer?
What will be an ideal response?
City streets, sewage systems, and police protection are all examples of:
A. public goods. B. private goods. C. exclusive goods. D. rival goods.
A monopoly has two production plants with cost functions C1 = 50 + 0.1Q12 and C2 = 30 + 0.05Q22. The demand it faces is Q = 500 ? 10P. What is the condition for profit maximization?
A. MC1(Q1 + Q2) = MC2(Q1 + Q2) = MR (Q1 + Q2). B. MC1(Q1 + Q2) = MC2(Q1 + Q2) = P (Q1 + Q2). C. MC1(Q1) = MC2(Q2) = MR(Q1 + Q2). D. MC1(Q1) = MC2(Q2) = P(Q1 + Q2).