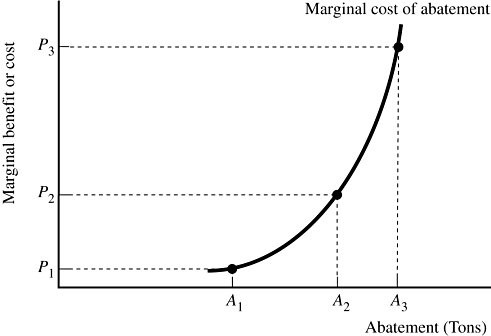
 A firm that generates pollution is illustrated in Figure 9.7. The government has chosen to impose a pollution tax equal to P2. From the firm's point of view, the marginal benefit of abatement is:
A firm that generates pollution is illustrated in Figure 9.7. The government has chosen to impose a pollution tax equal to P2. From the firm's point of view, the marginal benefit of abatement is:
A. avoiding the pollution tax imposed by the government.
B. the positive publicity the firm will receive by having a "green" production plant.
C. the reciprocal of the marginal cost of abatement.
D. zero because abatement benefits the general public, not the firm.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A perfectly competitive firm
A) sells a product that has perfect substitutes. B) has a perfectly inelastic demand. C) has a perfectly elastic supply. D) Answers A and B are correct. E) Answers A and C are correct.
Maryanne expects to work for another 30 years and expects to live another 10 years after she retires
If Maryanne completely smooths consumption over her lifetime, for every $1,000 increase in disposable income, she will use ________ for consumption each year. A) $100 B) $333 C) $667 D) $750
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. Under the gold standard, a nation experiencing chronic trade deficits had to increase its money supply while reducing its holdings of gold. 2. After World War II, most nations adopted some type of fixed or controlled exchange rate system. 3. Under a fixed or controlled exchange rate system, if the United States wanted to increase the value of the dollar, it could buy foreign currencies with dollars. 4. Since World War II, the importance of gold in international exchange has increased. 5. The Bretton Woods system included the idea of fixed exchange rates.
Cash and other assets that are expected to be converted to cash within one year are called
a. short-term assets b. long-term assets c. short-term liabilities d. long-term liabilities e. current assets