The equilibrium price in a competitive market
A. Remains unchanged forever.
B. Remains unchanged only if demand doesn't change.
C. Ensures that anyone who wants the good can get it.
D. Is the price at which the quantity of a good demanded in a given time period equals the quantity supplied.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Technical and organizational change
A) typically reduces prices by increasing the supply of the product, ceteris paribus. B) typically reduces prices by decreasing the demand for the product, ceteris paribus. C) typically increases prices by increasing the demand for the product, ceteris paribus. D) typically increases prices by decreasing the supply for the product, ceteris paribus.
Crowding out occurs when government deficit spending results in less private spending
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The "primary motive" of regulators, according to the share-the-gains, share-the-pains theory, is to
A. keep their jobs. B. ensure that every group gets what it wants. C. maximize their income through accepting monetary payoffs from groups. D. ensure that all customers share the benefits of regulation, and not just the wealthiest consumers.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 16.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 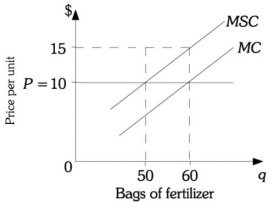 Figure 16.1 Refer to Figure 16.1. The ________ amount of fertilizer is 50 bags.
Figure 16.1 Refer to Figure 16.1. The ________ amount of fertilizer is 50 bags.
A. equitable B. efficient C. unregulated D. break-even