Refer to the figure. Assuming this market is representative of the economy as a whole, this economy:
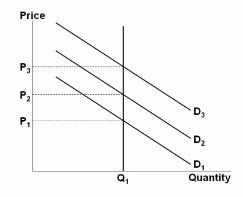
A. is highly susceptible to recessions and high unemployment.
B. faces regularly fluctuating output levels in response to demand shocks.
C. is capable of always producing at its optimal capacity.
D. can only lessen the impacts of business cycles through active government policy.
C. is capable of always producing at its optimal capacity.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 4-5. The figure above represents the market for pecans. Assume that this is a competitive market. If the price of pecans is $3, what changes in the market would result in an economically efficient output?
A) The price would increase, the quantity demanded would decrease, and the quantity supplied would increase. B) The price would increase, the demand would decrease, and the supply would increase. C) The price would increase, the quantity supplied would decrease, and the quantity demanded would increase. D) The quantity supplied would increase, the quantity demanded would decrease, and the equilibrium price would increase.
Whirlpool Corporation buys steel in sheets to manufacture refrigerators. Whirlpool also buys a new factory and a metal press to mold the steel. Which purchases are included in GDP?
a. the steel b. the steel, the factory, and the metal press c. the factory and the metal press d. the steel and the metal press
After the transaction in Table 13-1 is completed, what happens to actual reserves, required reserves, and excess reserves? Assume the required reserve ratio is 25 percent
a. Actual reserves increase by $10 million, required reserves increase $2.5 million, and excess reserves increase by $7.5 million. b. Actual reserves decrease by $10 million, required reserves decrease $2.5 million, and excess reserves decrease by $7.5 million. c. Actual reserves increase by $10 million, required reserves are unchanged, and excess reserves increase by $10 million. d. Actual reserves decrease by $10 million, required reserves decrease by $10 million, and excess reserves are unchanged.
In contrast to a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolist operates in the long run
A. at a price higher than marginal cost. B. with a profit equal to zero. C. at an efficient level of output. D. at the minimum point on its average total cost curve.