The figure shows two forces acting on an object, with magnitudes and What third force will cause the object to be in equilibrium (acceleration equals zero)?
A) 52 N pointing down
B) 52 N pointing up
C) 82 N pointing down
D) 82 N pointing up
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A Geiger counter is like an electroscope that discharges whenever ions formed by a radioactive particle produce a conducting path. A typical Geiger counter consists of a thin conducting wire of radius 0.002 cm stretched along the axis of a conducting cylinder of radius 2.0 cm. The wire and the cylinder carry equal and opposites charges of 8.0 × 10?10 C all along their length of 10.0 cm. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the surface of the wire?
What will be an ideal response?
The average force required to accelerate a 0.20-kg ball from rest to 30 m/s in 0.002 s is
A. 15,000 N. B. 3,000 N. C. 0.003 N D. 75,000 N.
In Procedure 1, what is the relationship between the velocity and the slope of the curve? (Hint: What are the units for the slope on the graph that you plotted?)
If p1 = 900 kPa, the force of the water on the nozzle is nearest:
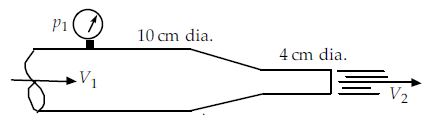
(A) 6910 N
(B) 6470 N
(C) 5120 N
(D) 4920 N