When interest rates in the U.S. decline, we can expect capital:
A. inflows and outflows to increase.
B. inflows and outflows to decrease.
C. outflow to decrease, and inflow to increase.
D. inflow to decrease, and outflow to increase.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The supply-side motivated tax cuts of 1981 during the Reagan administration were aimed at
A) balancing the federal budget. B) decreasing aggregate supply. C) increasing aggregate demand. D) increasing aggregate supply.
Refer to Table 4-8. Suppose that the quantity of labor demanded decreases by 40,000 at each wage level. What are the new free market equilibrium hourly wage and the new equilibrium quantity of labor?
A) W = $10.00; Q = 390,000 B) W = $8.50; Q = 340,000 C) W = $9.50; Q = 380,000 D) W = $8.00; Q = 350,000
A firm with a demand curve P = 10 - Q is a perfect price discriminating monopolist with zero marginal costs and fixed costs of 12. Consider the following two statements comparing the price discriminating case with a single price monopolist. 1) In this case consumers are better off as a group because more of the product is produced. 2) Producers are better off because they have higher profits. Which of the following comments about these statements is true? 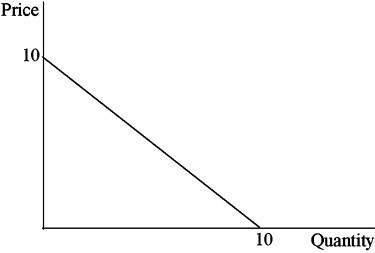
A. Only the second statement is true. B. Both statements are true. C. Both statements are false. D. Only the first statement is true.
Economic profit is most closely associated with:
A. the process of saving and investing. B. monopoly, innovation, and uninsurable risks. C. long-run competitive equilibrium. D. a static economy.